
Acute myeloid leukemia is the most common type of leukemia in adults. It is characterized by the pathological expansion of immature cells (myeloblasts) that invade the bone marrow and expand into the blood, affecting the production of the rest of the healthy cells. Although patients usually respond well to chemotherapy-based treatments, a large proportion of them eventually relapse or show resistance to these procedures.
The cause of relapse or resistance to treatment is sometimes due to the existence of leukemic stem cells capable of starting cancer again, and in turn, for being resistant to chemotherapy. However, identifying them is a challenge since there are no specific markers to detect and isolate them.
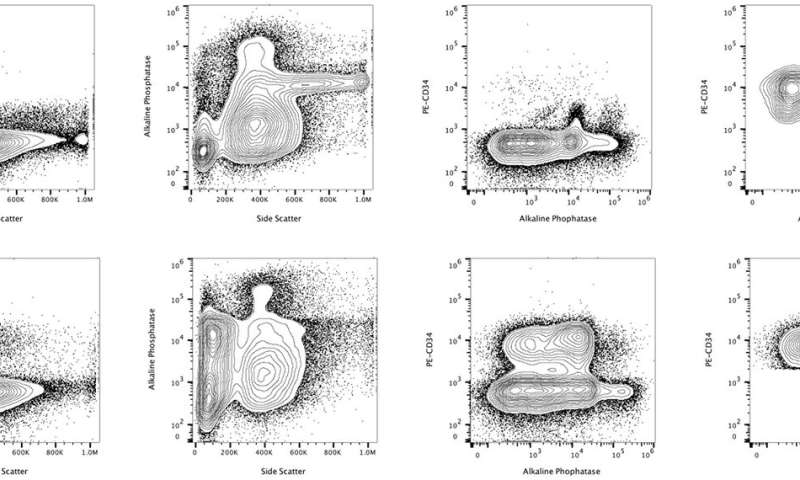
The Functional Cytomics Research Group at the Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute has developed innovative trials that allow the identification of these cells by testing the activity of a protein, alkaline phosphatase, present in myeloblasts.
To do this, they have used advanced cytomical methodologies that allow multiple functional characteristics to be analyzed cell by cell, individually, in a very few minutes.
The researchers identified a group of patients whose leukemic cells had high levels of alkaline phosphatase activity and another group of patients with lower levels of this activity. Both groups showed a differential response to chemotherapy treatment, with the most active phosphatase group showing the worst reaction to treatment and the shortest survival. Surprisingly, no significant association was detected between the results obtained through different cytogenetic analysis techniques and molecular studies, with the determination of prognostic factors of greater or lesser risk.
Source: Read Full Article