
NHS: Expert gives advice on treatment of chlamydia
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
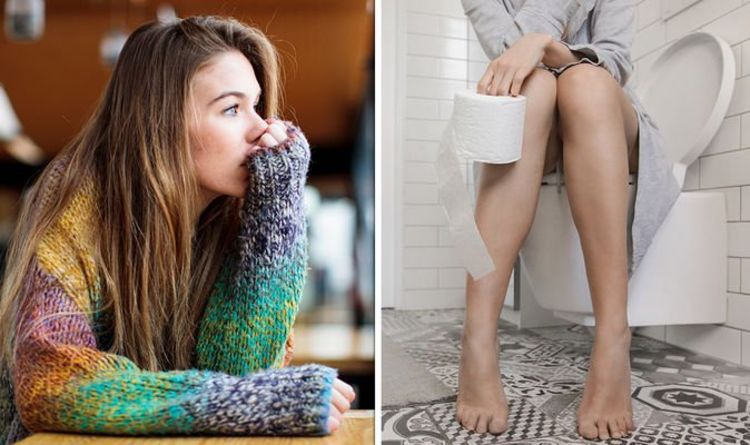
One warning sign of chlamydia is painful urination, for either gender, the NHS confirmed. Another indication is “unusual discharge” from the genital regions, including the bottom. For women, pain may be experienced in the stomach, which may be accompanied by bleeding between periods or after sex. For men, pain and swelling might occur in the testicles. However, the condition can persist with no apparent symptoms.
Symptoms can take up to three weeks from the initial infection to emerge.
“For some people they don’t develop until many months later,” the NHS stated.
Chlamydia, however, may not lead to any noticeable symptoms so testing can be crucial.
In fact, for 70 percent of women, chlamydia doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms.

Testing can be arranged via a pharmacy online, a GP surgery, community contraceptive service or a local genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinic.
This will usually involve taking a urine sample or a genital swab test.
What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection that is spread through sex or contact with infected genital fluids.
It is spread through unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex, as well as sharing sex toys.
Chlamydia can even spread without penetration, orgasm, or ejaculation, as genital contact is all that is needed to spread the infection.
“It can also be passed by a pregnant woman to her baby,” the NHS added.
Chlamydia, however, can not be passed on through kissing or hugging.
Furthermore, the infection is not passed on through sharing towels, swimming pools, toilet seats, or cutlery.
While the infection is easily treated with a short course of antibiotics, if not treated, serious consequences can develop.
The bacterial infection can spread throughout the body; for instance, in men chlamydia can spread to the testicles and epididymis.
The epididymis is the tube that carries sperm from the testicles.
In women, chlamydia may cause pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility.
“It can also sometimes cause reactive arthritis in men and women,” the health service added.
Reactive arthritis is when the joints, eyes, or urethra become inflamed, stiff and painful.
As such, knees, feet, toes, hips, or ankles may become red and swollen.
Treatment tends to focus on antibiotics, painkiller, and medications.
Source: Read Full Article